
Which materials are bad for mobile phone coverage?
Some materials should be used as little as possible when constructing a new building.

Different materials can interfere with mobile phone signals, reducing their strength or blocking them entirely. Here’s a look at some common culprits:


Interior walls and ceilings often use plasterboard, which can block signals to some extent. Even a small reduction in signal strength can be noticeable, especially if the initial signal is weak.

Fiberglass insulation in walls and attics can interfere slightly with mobile signals. Combined with plasterboard, the signal can be reduced by up to 4 dB, cutting signal strength by 50%.

Contrary to popular belief, clear glass doesn’t guarantee a good signal. While glass allows some signals to pass, double-insulated windows can reflect signals away. For better reception, opening a window or stepping outside is more effective.

OSB, a type of sheet material, can reduce mobile signals. If non-waterproof OSB gets wet, it can absorb water like a sponge and attenuate the signal by up to -20 dB.

Solid wood floors and walls block signals effectively. Different types of wood like beech, oak, mahogany, and maple are particularly good at absorbing signals. Thicker wood means more signal reduction.

Gypsum-based plastering, even in thin layers, can significantly affect signal strength. Adding OSB or plasterboard increases this effect.
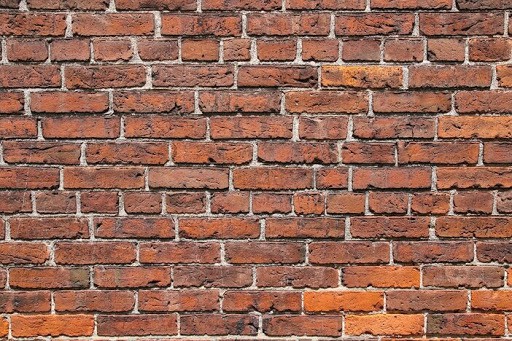
Brick walls are excellent at blocking signals due to their thickness and the mortar between the bricks. Additional materials inside walls, like metal and electronics, further obstruct signals.

Common in modern buildings, concrete and cement are robust materials that block and absorb radio signals, posing challenges for indoor signal strength in urban areas.

Energy-efficient materials like solar control glass, with metal coatings, significantly block signals to maintain indoor temperature, further reducing mobile signal strength.

Metals such as aluminium, lead, copper, steel, and iron are the biggest signal blockers. Metal roofs and interiors necessitate the use of GSM amplifiers to boost signal strength.
For more information on how to improve mobile phone coverage in your area, explore our solutions.

Some materials should be used as little as possible when constructing a new building.

Upgrade to 4G and 5G for faster, more secure business connectivity. Reliable, scalable, and future-proof—discover Mercuron’s solutions today!

It is not always easy to find a solution, so that’s where we come in!

Mercuron, a Belgian company, specializes in wireless communication. With our expertise in radio waves, we create ASTRID and mobile phone signal amplifiers from the ground up.